Don't miss our holiday offer - 20% OFF!
The use of technology in agriculture is becoming increasingly essential, with soil sensors emerging as one of the most vital tools for optimizing crop yield. These sensors help farmers monitor soil conditions in real-time, playing a key role in maintaining soil health and crop quality. This article will discuss the types of soil sensors, how they work, their benefits, and a practical guide to using sensors to monitor agricultural soil health.
Contents
What Are Soil Health Sensors?
Read More: Soil Nutrient Monitoring Technology for Nutrient Balance
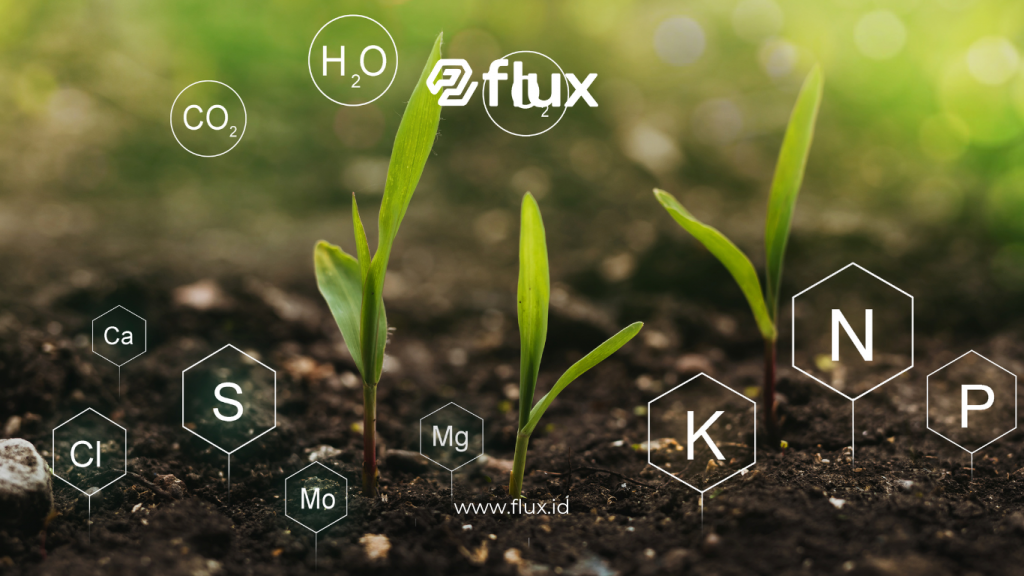
Soil health sensors are devices designed to measure various critical parameters in the soil, such as moisture, temperature, pH, nutrient levels, and salinity. This data helps farmers gain deeper insights into soil conditions and take appropriate actions to improve soil health, ultimately supporting optimal plant growth.
Types of Soil Sensors
Here are some commonly used soil sensors in agriculture:
- Soil Moisture Sensor: Measures moisture levels to assess plant water needs.
- Soil pH Sensor: Determines soil acidity or alkalinity, crucial for plant growth.
- Soil Temperature Sensor: Monitors soil temperature, which affects plant physiological processes.
- Soil Nutrient Sensor: Measures main nutrients in the soil, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Soil Salinity Sensor: Measures salt levels in the soil, which can impact plant growth.
How Soil Sensors Work in Monitoring Health

Read More: Soil Nutrient Sensors: A New Way to Measure Nutrient Content in Real-Time
Soil sensors work by detecting specific parameters within the soil and converting them into measurable data for analysis. For instance, a soil moisture sensor gauges the amount of water in the soil and outputs moisture values as a percentage. These sensors are usually connected to IoT systems, allowing data to be collected automatically and in real-time. Sensor data is then transmitted to monitoring devices or cloud-based applications, enabling remote monitoring.
Benefits of Using Soil Sensors in Agriculture
Using soil sensors in agriculture provides many benefits:
- Enhances Irrigation Efficiency: Moisture sensors help determine water needs, optimizing water usage.
- Optimizes Fertilization: Nutrient and pH sensors help farmers decide on the right type and amount of fertilizer.
- Reduces Operational Costs: Accurate monitoring helps reduce water and fertilizer use, lowering operational costs.
- Increases Crop Productivity and Quality: With soil condition data, farmers can maintain soil health for better crop yields.
- Detects Problems Faster: Sensor data allows for early detection of soil issues, such as drought or nutrient deficiencies.
Guide to Using Sensors to Monitor Soil Health

Read More: Optimizing Agriculture with Soil Health Monitoring Sensors
Here are practical steps for using soil sensors to monitor agricultural soil health:
1. Preparing and Installing the Sensor
- Choose the type of sensor that suits your land and crop needs.
- Determine the installation points in the field, usually near the plant roots.
- Ensure the sensor is placed at the correct depth to obtain accurate results.
2. Sensor Calibration
- Conduct initial calibration based on the soil conditions at the site.
- Adjust sensor settings to the desired parameters, such as moisture or pH.
3. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- Use a device or application connected to the sensor to monitor data in real-time.
- Regularly check soil conditions to observe the impact of weather or irrigation.
4. Making Data-Driven Decisions
- Analyze the data to make informed decisions. For instance, if soil moisture is low, irrigate to maintain soil conditions.
- Use pH or nutrient data to determine suitable fertilization.
5. Periodic Evaluation and Adjustments
- Conduct regular evaluations based on monitoring results.
- Adjust farming strategies, such as fertilization and irrigation, to maintain soil health.
Tips for Choosing the Right Soil Sensor
- Match the Sensor to Your Needs: Choose a sensor based on the parameters you want to measure, such as moisture, temperature, or pH.
- Consider Accuracy and Durability: Opt for sensors with high accuracy and durability to withstand field conditions.
- IoT Integration Capability: Sensors that can be integrated with IoT systems enable remote monitoring.
- Ease of Use: Sensors that are easy to install and operate save time and effort.
- Price and Spare Part Availability: Select a sensor that fits your budget and ensure that spare parts are readily available if needed.
Conclusion
Using sensors to monitor soil health is an effective innovation for improving agricultural productivity. These sensors help farmers understand soil conditions in real-time, enabling them to take the right actions to maintain soil quality. With soil sensors, farmers can optimize water and fertilizer use while reducing operational costs.
In the era of modern agriculture, soil sensors have become an essential tool in enhancing yield efficiently and sustainably. This technology brings positive change to agriculture, making land management smarter and more eco-friendly.





