Don't miss our holiday offer - 20% OFF!
In today’s digital era, technology increasingly plays a crucial role in improving efficiency and accuracy across various fields. One technology that is becoming more widely adopted is RFID (Radio Frequency Identification). Particularly in the financial sector, RFID offers an effective solution for asset and inventory management. This article will explain how RFID card sensors work and how this technology can enhance asset management in the Finance Department.
Contents
What is RFID?

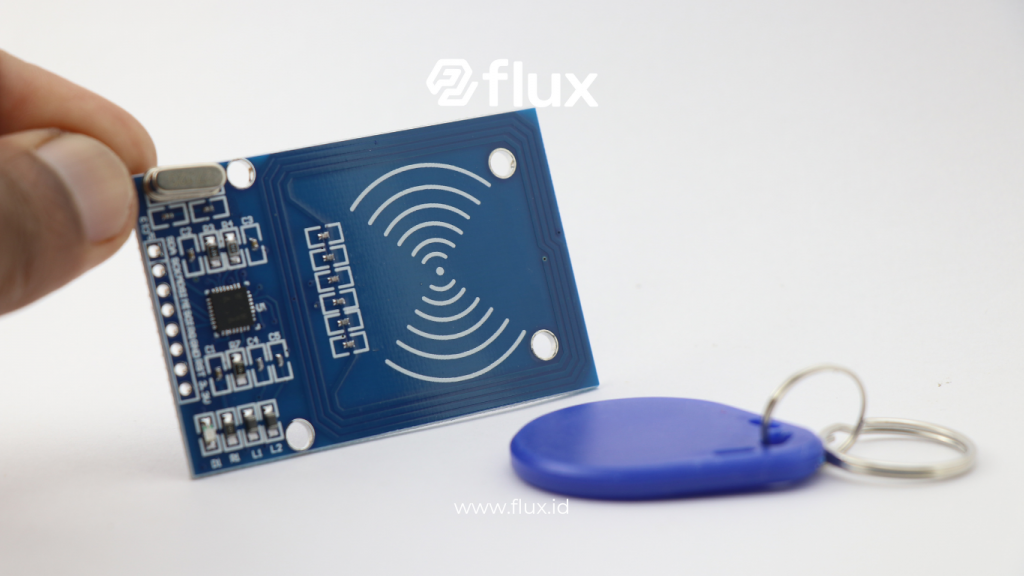
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify and track objects. RFID works by using tags attached to objects and RFID readers that can read information from these tags without requiring physical contact.
Key Components of RFID
- RFID Tag: This is the component attached to the object to be tracked. RFID tags consist of a chip that stores data and an antenna that allows communication with the reader.
- RFID Reader: This device reads the data stored in the RFID tag. The reader sends a radio signal to the tag and receives a response from the tag.
- Antenna: The antennas on both the tag and reader enable data transmission through radio waves.
- Middleware: Software that manages data from the RFID readers and integrates this information into a larger system.
How RFID Card Sensors Work

Read More: How Security Sensors Safeguard Government Financial Assets
- Attaching RFID Tags to Assets
The first step in RFID implementation is attaching tags to assets or inventory. RFID tags can be cards, stickers, or other forms suitable for the needs. These tags store important information about the asset, such as identification numbers, type, and location.
- RFID Reader Accesses Data
When an RFID tag is within the range of an RFID reader, the reader sends a radio signal to activate the tag. The tag then sends the stored data back to the reader. This process occurs in milliseconds and does not require direct contact.
- Data Processing
Data received from the RFID reader is then processed by middleware. Middleware is responsible for integrating information from various RFID readers into an inventory or asset management system. This data can be used to update records, track locations, and manage asset status.
- Information Updates and Reporting
Once the data is processed, the latest information about the assets becomes available in the management system. This allows the Finance Department to monitor assets in real-time, conduct automatic inventory checks, and generate accurate reports on asset status.
Benefits of Using RFID in the Finance Department

Read More: How Security Sensors Support Financial Departments
- Time Efficiency
RFID reduces the time needed to identify and track assets. By automating processes, the Finance Department can speed up inventory checks and asset monitoring.
- High Accuracy
RFID technology reduces the likelihood of human error in recording and tracking assets. The collected data is accurate and reliable, enhancing the quality of managerial information.
- Cost Savings
Although the initial investment in RFID technology may be high, in the long run, RFID can reduce operational costs. Cost savings can come from reduced asset loss, increased efficiency, and decreased manual labor.
- Ease of Integration
RFID can be integrated with existing management systems, such as ERP systems or inventory software. This allows the Finance Department to leverage new technology without needing to replace the entire existing system.
- Increased Security
RFID enables real-time asset tracking and can help prevent asset loss or theft. Information about the location and status of assets can be accessed anytime, enhancing security oversight.
Implementing RFID in the Finance Department
Read More: Government Financial Optimization with IoT Sensors
- Planning and Evaluating Needs
Before implementing RFID, it is important to conduct a needs assessment and thorough planning. Identify the assets to be tagged with RFID and determine the type of tags and readers required.
- Installation and Configuration
After planning, the next step is to install RFID tags on assets and configure the RFID readers. Ensure that tags are correctly placed and readers are calibrated to optimize performance.
- User Training
Training staff on how to use the RFID system is crucial. Ensure that all users understand how RFID works and how to operate the system to maximize the benefits of this technology.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation
Once the RFID system is implemented, perform ongoing monitoring and evaluations to ensure the system functions correctly. Address any issues that arise and make necessary improvements.
Conclusion
RFID technology offers an effective solution for improving asset and inventory management in the Finance Department. With time efficiency, high accuracy, and cost savings, RFID is an excellent choice for modernizing asset management systems. Proper implementation of this technology can help the Finance Department manage assets more effectively, increase security, and provide accurate information for decision-making.
By following proper planning, installation, and evaluation steps, the Finance Department can fully leverage the potential of RFID to achieve better asset management. This technology not only enhances operational efficiency but also provides long-term benefits for improved and smarter inventory management.





