Don't miss our holiday offer - 20% OFF!
Technological innovation is now playing a pivotal role in modern agriculture, especially with the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. This innovative solution enables farmers to monitor and manage fields, crops, and even livestock using interconnected smart devices. Here, we’ll explore how IoT actively helps reduce waste and increase productivity in the agricultural sector.
Contents
What is IoT in Agriculture?

Read More: IoT Sensors in Agriculture: Monitoring Plant Health in Real-Time
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of devices that connect and communicate with each other to exchange data, enabling automated decisions. In agriculture, IoT solutions monitor and control environmental factors such as soil moisture, air temperature, crop health, and nutrient needs. These tools empower farmers to manage resources more effectively on both small and large scales.
Benefits of IoT in Agriculture
- Efficient Land Management
IoT allows farmers to monitor soil conditions, such as moisture and nutrient levels, with precision. Using this data, they can optimize planting strategies to match optimal conditions, reducing the excessive use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides. - Optimized Irrigation
Smart irrigation systems equipped with IoT sensors adjust watering frequency and volume based on real-time soil moisture data. This technology conserves water and reduces energy costs associated with irrigation, which is especially useful in regions with limited water resources. - Crop and Health Monitoring
With sensors placed in fields, farmers receive updates on crop health in real-time. These sensors detect early signs of disease or pest infestation, allowing for prompt intervention, which increases the chances of a healthy, productive harvest. - Weather and Environmental Analysis
IoT enables farmers to access detailed weather and environmental data, helping them make informed decisions about planting and harvesting while better preparing for extreme weather conditions. - Product Storage and Distribution
IoT systems also aid in maintaining product quality during storage and distribution. Sensors monitoring temperature and humidity ensure that produce remains fresh until it reaches consumers, helping to reduce post-harvest waste.
How Does IoT Work in Agriculture?
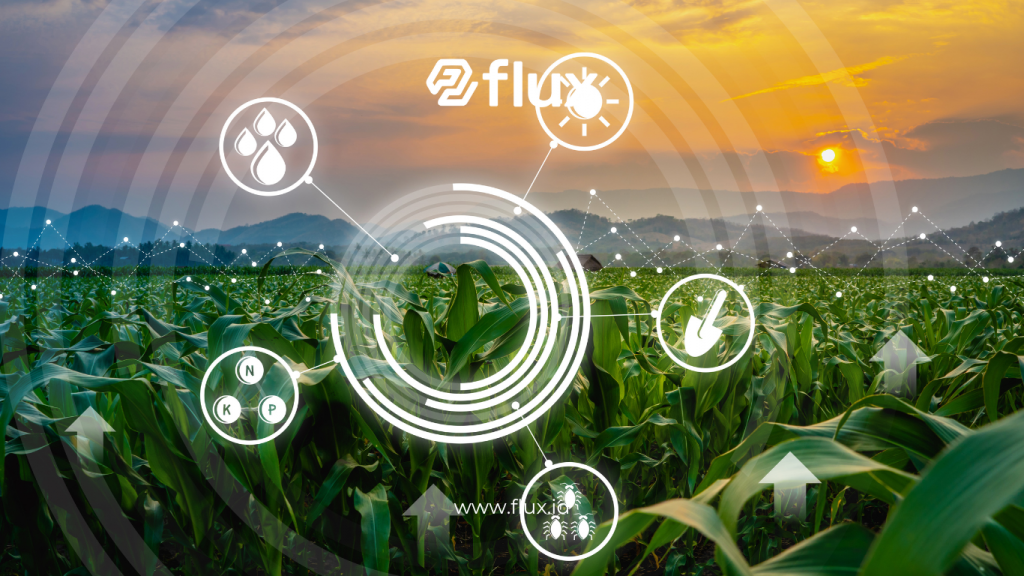

Read More: Optimizing Modern Agriculture: The Role of IoT in Enhancing Harvest Yields
IoT in agriculture operates through a blend of hardware, software, and connectivity. The essential components in an IoT-based agricultural ecosystem include:
- Sensors and Data Collection Devices
Sensors measure various environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and soil nutrient levels. These devices actively collect data, which is then sent to an analysis center. - Data Connectivity
Internet or dedicated network connectivity enables the data collected by field sensors to reach a cloud or central server. Technologies such as 5G and low-power wide-area (LPWA) networks facilitate long-distance data transmission. - Data Analysis Platforms
After data is collected, analysis software processes it to deliver actionable insights to farmers. These platforms can offer suggestions based on identified patterns or trends. - Automation and Remote Control
In addition to providing recommendations, IoT systems enable process automation, allowing farmers to control irrigation or fertilization remotely through mobile applications.
Challenges in Implementing IoT in Agriculture

Although IoT brings significant advantages, its application in agriculture still encounters several challenges, including:
- High Initial Investment
Implementing IoT requires substantial investment in sensors, networks, and analysis platforms. Many small-scale farmers struggle to afford a comprehensive IoT setup. - Limited Network Infrastructure
Reliable connectivity is crucial for IoT functionality, but some rural areas still lack adequate network infrastructure, which limits IoT’s reach. - Technological Complexity
Operating IoT systems can be technically demanding, and not all farmers have the necessary skills. Training programs are needed to help them understand and maximize the technology’s benefits. - Data Security Risks
IoT-based agriculture generates large volumes of data stored online, making it vulnerable to cybersecurity risks that must be carefully managed.
Examples of IoT Applications in Agriculture
- Smart Farming in Rice Fields
In Indonesia, IoT technology is transforming rice fields by optimizing irrigation. Sensors measure soil moisture in real-time, ensuring irrigation is only applied as needed. - Smart Livestock Management
IoT also benefits livestock farming by monitoring animal health. Barn sensors track temperature, humidity, and animal activity to detect early signs of illness. - Automated Pest Control
IoT-enabled camera sensors identify pest types attacking crops, allowing farmers to schedule pesticide applications more accurately and effectively. - Greenhouse Monitoring
IoT sensors in greenhouses monitor temperature, humidity, and light, allowing farmers to maintain ideal conditions year-round without frequent manual checks.
The Future of IoT in Agriculture
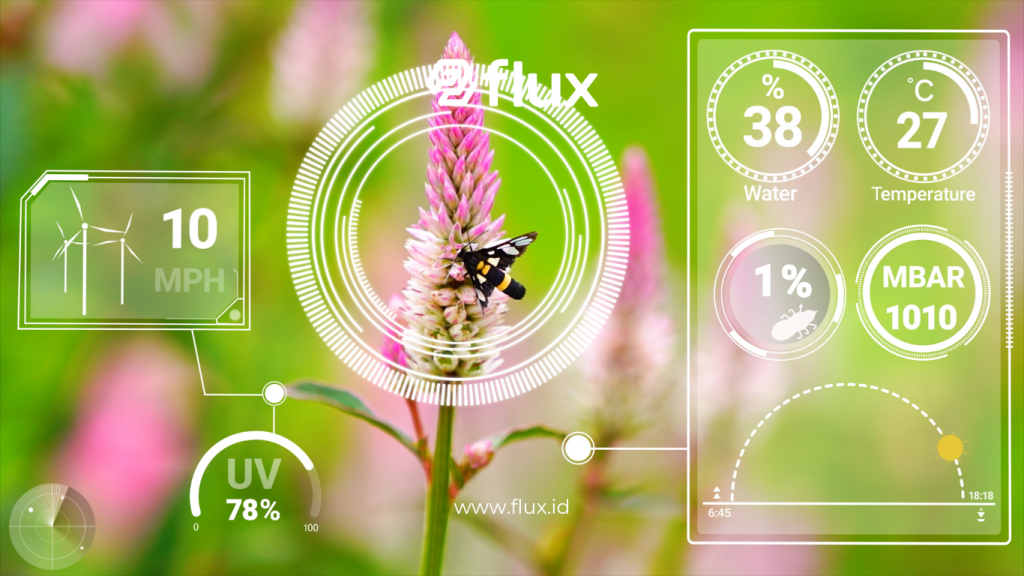
Read More: Complete Guide: Implementing IoT Sensors for Smart Agriculture Monitoring and Irrigation Management
IoT’s potential in agriculture continues to grow as technological and network advancements accelerate. Trends likely to enhance IoT’s adoption in agriculture include:
- AI for Predictive Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) will play an essential role in analyzing IoT data for more accurate predictions, such as optimal planting and harvesting times. - 5G Networks
The rollout of 5G networks will improve connectivity speed and reliability, especially in remote agricultural areas. - Robotics and Drones
IoT-equipped drones can monitor large areas quickly, while agricultural robots aid in crop management and harvesting automation.
Conclusion
The implementation of IoT in agriculture has profoundly impacted waste reduction and productivity improvements. This technology allows farmers to make more informed decisions using data, such as adjusting irrigation and monitoring crop health in real-time. While IoT adoption still faces challenges like costs and infrastructure limitations, continuous advancements promise to make it more accessible and affordable. With increasing adoption, IoT is rapidly becoming a vital tool for achieving food security and sustainability, marking a new era in modern agriculture.





